4-Pattern-Recognition
Pattern recognition
© Haodong Li haodongli@zju.edu.cn
- Pattern recognition
cvzoneandmediapipe
Pattern recognition
- Template matching is one of the most primitive and basic pattern recognition methods. It studies where the pattern of a specific object is located in the image, and then recognizes the object. This is a matching problem
- The principle of template matching is very similar to that of convolution
- The template slides from the origin on the original image, and the difference between the template and the image covered by the template is calculated.
cv.TM_SQDIFF
\[R(x, y)=\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)-I\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right)^{2}\]cv.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED
\[R(x, y)=\frac{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)-I\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right)^{2}}{\sqrt{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} T\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)^{2} \cdot \sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} I\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)^{2}}}\]cv.TM_CCORR
\[R(x, y)=\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right) \cdot I\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right)\]cv.TM_CCORR_NORMED
\[R(x, y)=\frac{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T^{}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right) \cdot I^{}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right)}{\sqrt{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} T^{}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)^{2} \cdot \sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} I^{}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)^{2}}}\]cv.TM_CCOEFF
\[\begin{gathered} R(x, y)=\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T^{\prime}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right) \cdot I^{\prime}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right) \\ T^{\prime}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)=T\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)-1 /(w \cdot h) \cdot \sum_{x^{\prime \prime}, y^{\prime \prime}} T\left(x^{\prime \prime}, y^{\prime \prime}\right) \\ I^{\prime}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)=I\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)-1 /(w \cdot h) \cdot \sum_{x^{\prime \prime}, y^{\prime \prime}} I\left(x+x^{\prime \prime}, y+y^{\prime \prime}\right) \end{gathered}\]cv.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED
\[R(x, y)=\frac{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}}\left(T^{\prime}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right) \cdot I^{\prime}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)\right)}{\sqrt{\sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} T^{\prime}\left(x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}\right)^{2} \cdot \sum_{x^{\prime}, y^{\prime}} I^{\prime}\left(x+x^{\prime}, y+y^{\prime}\right)^{2}}}\]import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.colors as mat_color
def read_image(path="./images/wu.jpg", flags=cv2.IMREAD_COLOR):
img_bgr = cv2.imread(path)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
print(img_rgb.shape)
return img_rgb
no_norm = mat_color.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=255, clip=False)
img_wu = read_image()
plt.imshow(img_wu, norm=no_norm)
(378, 668, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a01f818a90>
img_wu_tem = read_image("./images/wu_tem.jpg")
plt.imshow(img_wu_tem, norm=no_norm)
(66, 57, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a01f927910>

width, height = img_wu_tem.shape[0], img_wu_tem.shape[1]
methods = [cv2.TM_CCOEFF, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED, cv2.TM_CCORR,
cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED, cv2.TM_SQDIFF, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED]
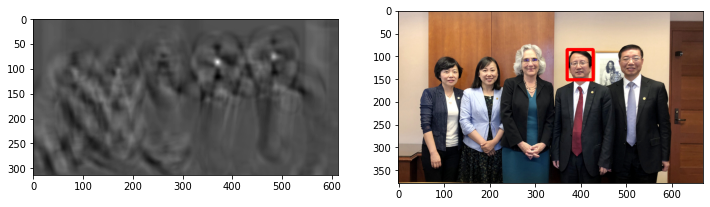
def show_wu_face(mathod, color=(255, 0, 0)):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_wu, img_wu_tem, mathod)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(res, cmap = 'gray')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
print(min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc)
top_left = min_loc if mathod in [cv2.TM_SQDIFF, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED] else max_loc
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + height, top_left[1] + width)
img_wu_detect = cv2.rectangle(np.copy(img_wu),
top_left, bottom_right, color, 5)
plt.imshow(img_wu_detect, norm=no_norm)
show_wu_face(methods[0])
-21032008.0 47274936.0 (370, 116) (370, 86)
show_wu_face(methods[1], (0, 255, 0))
-0.4156877100467682 0.9993270635604858 (370, 116) (370, 86)

print("This is a bad algorithm")
show_wu_face(methods[2], (0, 0, 255))
This is a bad algorithm
7438519.5 326176640.0 (470, 312) (537, 59)

show_wu_face(methods[3], (0, 255, 255))
0.29923704266548157 0.9998716115951538 (88, 292) (370, 86)
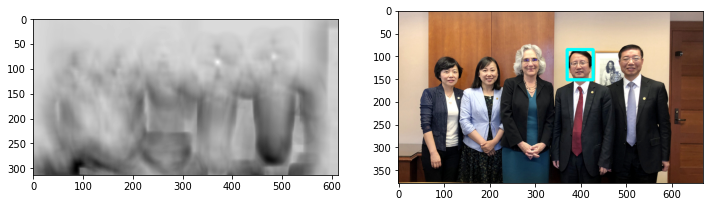
show_wu_face(methods[4], (255, 255, 0))
63684.0 233722720.0 (370, 86) (470, 312)
show_wu_face(methods[5], (255, 0, 255))
0.0002567677292972803 1.0 (370, 86) (607, 22)
img_ma = read_image("./images/mario.jpg")
plt.imshow(img_ma, norm=no_norm)
(900, 1600, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a021e25550>

img_tem = read_image("./images/coin.png")
plt.imshow(img_tem, norm=no_norm)
(106, 91, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a0227f37f0>

width, height = img_tem.shape[0], img_tem.shape[1]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_ma, img_tem, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
threshold = 0.4
loc = np.where(res >= threshold)
img_ma_copy = np.copy(img_ma)
print(loc)
for pt in zip( * loc[::-1]):
cv2.rectangle(img_ma_copy, pt, (pt[0] + height, pt[1] + width), (255, 0, 0), 3)
def show_mario(res, img):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(res, cmap = 'gray')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img, norm=no_norm)
(array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 488, 488, 488], dtype=int64), array([1238, 1239, 1240, ..., 774, 775, 776], dtype=int64))
show_mario(res, img_ma_copy)

img_ma_copy = np.copy(img_ma)
last_width = 0
points = [pt for pt in zip( * loc[::-1])]
points = sorted(points, key=lambda x:x[0])
last_width = 0
for pt in points:
if np.abs(pt[0] - last_width) < 50:
continue
last_width = pt[0]
cv2.rectangle(img_ma_copy, pt, (pt[0] + height, pt[1] + width), (255, 0, 0), 3)
show_mario(res, img_ma_copy)

Solve by Image Gradient?
- All the above algorithms compare the similarity by calculating the pixel value
- Too rigid, inflexible, sometimes naive
- Not universal
- Not robust
- Use image gradient to illustrate similarity
- More robust and universal
img_wu_2 = read_image("./images/wu_2.jpeg")
plt.imshow(img_wu_2, norm=no_norm)
(533, 799, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a020d9fd30>

img_wu_3 = read_image("./images/wu_4.jpg")
plt.imshow(img_wu_3, norm=no_norm)
(577, 868, 3)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a020c5f4c0>

# On line 3 we load the sift algorithm.
# On lines 4 and 5 we find the keypoints and descriptors of the original image
# and of the image to compare.
sift = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
kp_1, desc_1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img_wu_2, None)
kp_2, desc_2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img_wu_3, None)
# On lines 10, 11 and 12 we load `FlannBasedMatcher` which is
# the method used to find the matches between the descriptors of the 2 images.
# On line 13 we find the matches between the 2 images.
# We’re storing the matches in the array ‘matches’.
index_params = dict(algorithm=0, trees=5)
search_params = dict()
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params, search_params)
matches = flann.knnMatch(desc_1, desc_2, k=2)
print("Number of matches ->", len(matches))
Number of matches -> 886
# In this part we apply the ratio test to select only the good matches.
# The quality of a match is define by the distance.
# The distance is a number, and the lower this number is,
# the more similar the features are.
good_points = []
ratio = 0.88
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < ratio * n.distance:
good_points.append(m)
print("Number of good_points ->", len(good_points))
img_wu_res = cv2.drawMatches(img_wu_2, kp_1, img_wu_3, kp_2, good_points, None)
Number of good_points -> 146
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
plt.imshow(img_wu_res, norm=no_norm)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a020a08640>

img_wu_res_ones = cv2.drawMatches(np.ones(img_wu_2.shape, dtype=np.uint8), kp_1,
np.ones(img_wu_3.shape, dtype=np.uint8), kp_2,
good_points, None)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
plt.imshow(img_wu_res_ones, norm=no_norm)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1a020ac2280>

def draw_key_pts(good_points, img_2, img_3):
list_kp_1 = [kp_1[mat.queryIdx].pt for mat in good_points]
list_kp_2 = [kp_2[mat.trainIdx].pt for mat in good_points]
for pt in list_kp_1:
pt = (round(pt[0]), round(pt[1]))
img_2 = cv2.circle(img_2, pt, 5, (255, 0, 0), -1)
for pt in list_kp_2:
pt = (round(pt[0]), round(pt[1]))
img_3 = cv2.circle(img_3, pt, 5, (255, 0, 0), -1)
return img_2, img_3
def show_img_den(img_2, img_3, group=None):
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img_2, group, norm=no_norm) if group is not None else plt.imshow(img_2, norm=no_norm)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_3, group, norm=no_norm) if group is not None else plt.imshow(img_3, norm=no_norm)
img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3 = draw_key_pts(good_points,
img_2=np.zeros(img_wu_2.shape, dtype=np.uint8),
img_3=np.zeros(img_wu_3.shape, dtype=np.uint8))
show_img_den(img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3)
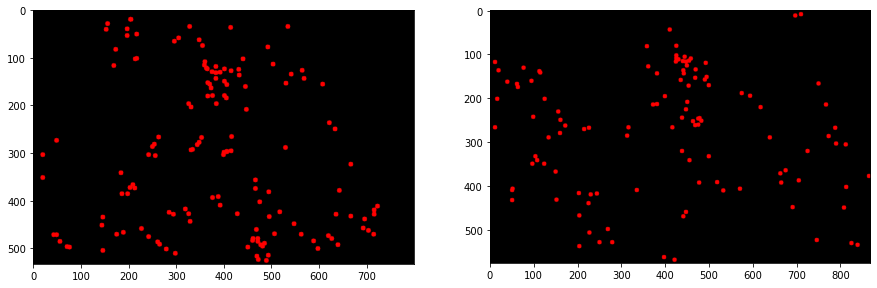
img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3 = draw_key_pts(good_points,
np.copy(img_wu_2), np.copy(img_wu_3))
show_img_den(img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3)

def filter_process(good_points, img_2_shape, img_3_shape, radius=2,
kernel_size=75, lightness_rate=1.0):
list_kp_1 = [kp_1[mat.queryIdx].pt for mat in good_points]
list_kp_2 = [kp_2[mat.trainIdx].pt for mat in good_points]
def filter_process_single(list_kp, img, radius=radius,
kernel_size=kernel_size, lightness_rate=lightness_rate):
for pt in list_kp:
pt = (round(pt[0]), round(pt[1]))
img = cv2.circle(img, pt, radius, (255, 255, 255), -1)
img = cv2.boxFilter(img, -1, (kernel_size, kernel_size), normalize=True)
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
pixel_value = min(round((img[i][j] - 0) * lightness_rate), 255)
img[i][j] = pixel_value
return img
img_2 = filter_process_single(list_kp_1, np.zeros(img_2_shape, dtype=np.uint8))
img_3 = filter_process_single(list_kp_2, np.zeros(img_3_shape, dtype=np.uint8))
return img_2, img_3
img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3 = filter_process(good_points, img_wu_2.shape[:2],
img_wu_3.shape[:2], lightness_rate=9.0)
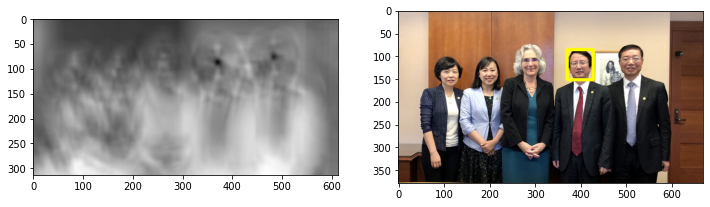
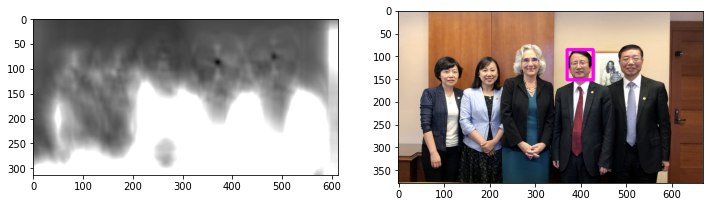
show_img_den(img_wu_den_2, img_wu_den_3, group="gray")

def detect_process(img_wu_den, img_ori, radius_rate=1.0):
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(img_wu_den)
radius = max(round(max_val * radius_rate), 100)
print(min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc, radius)
img_wu_detect = cv2.circle(np.copy(img_ori), max_loc, radius, (255, 0, 0), 5)
return img_wu_detect
img_wu_detect_2 = detect_process(img_wu_den_2, np.copy(img_wu_2))
img_wu_detect_3 = detect_process(img_wu_den_3, np.copy(img_wu_3))
show_img_den(img_wu_detect_2, img_wu_detect_3)
0.0 108.0 (0, 0) (395, 143) 108
0.0 99.0 (0, 0) (457, 123) 100

cvzone and mediapipe
The End
2022.4